zhihao
Solar-Powered Robots are the Sustainable Answer to a Cleaner, Connected Planet
Solar energy is virtually unlimited and one of the cleanest forms of renewable power. So building machines driven by the sun makes perfect environmental sense.
Solar-powered robots and drones are busy pushing technological boundaries in flight and space exploration, but they are also making light work of everything from farming to cleaning up the planet.
In communications and earth observation, high-altitude solar drones do the work of satellites without the high cost of space launches. Autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) powered by solar panels during daylight and batteries at night, may be airborne for months or even years at a time.
Google’s Project Skybender is using thousands of solar-powered drones, each with a wingspan up to 160 feet (50 meters) to deliver gigabits-per-second 5G networks. And solar drone technology is being pushed to new limits with the PHASA-35 UAV, designed to fly for up to a year at altitudes above 55,000 feet.
Higher still are the solar-powered moon rovers slated by NASA to help find water on the lunar surface. When they get there, MoonRanger and its smaller mission buddy CubeRover will provide support to astronauts, carrying out missions including exploring for ice and transporting cargo.
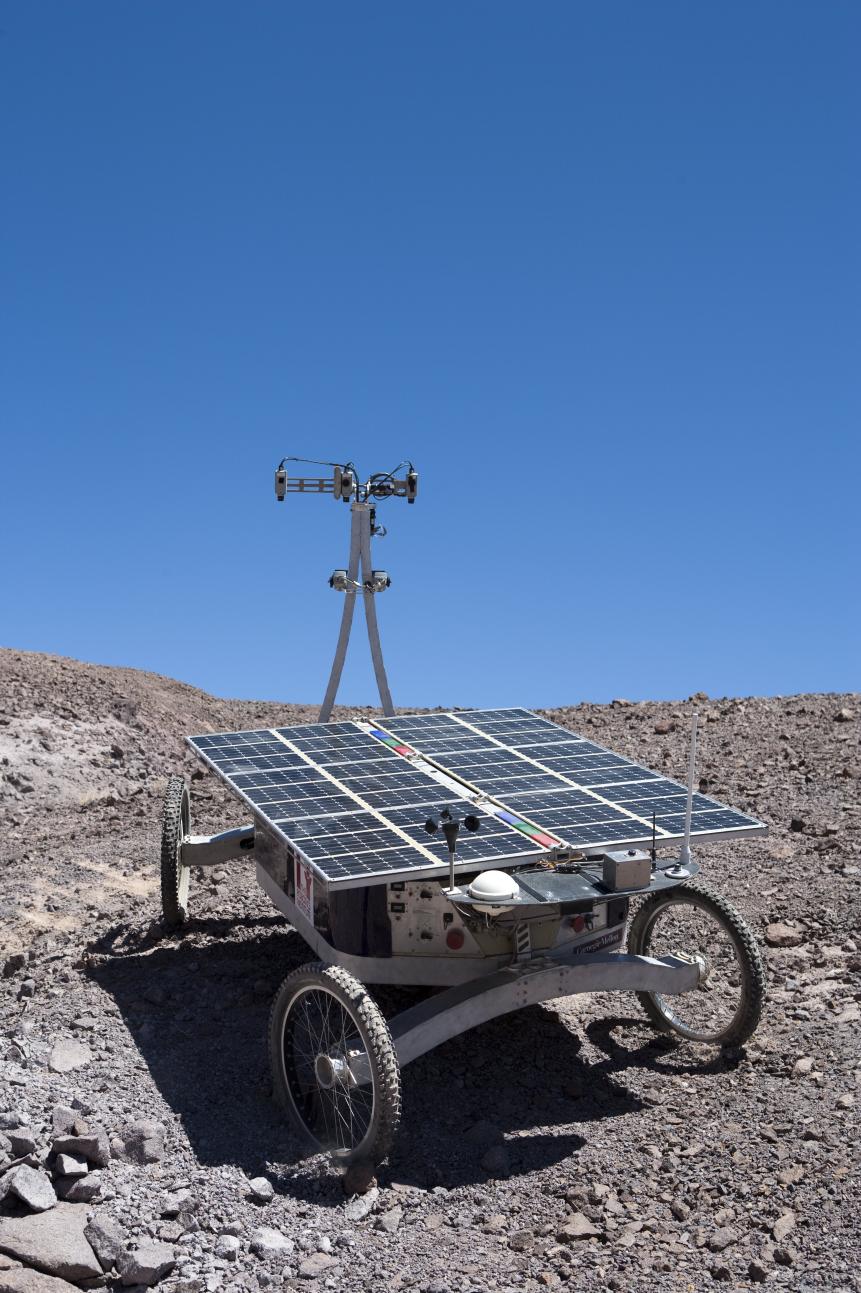

John B. Carnett
Engineers from Carnegie Mellon University developed this robot rover using solar energy, named Zoe, to detect life on seemingly lifeless environments.
Meanwhile, robotic explorers equipped with solar panels are mapping the Earth’s oceans. Saildrone has launched a fleet of autonomous boats using the sun to power sensors that measure weather conditions, water chemistry, carbon dioxide levels, and marine life.
Three drones departed New Zealand in January 2019 to make the first ever autonomous circumnavigation of Antarctica, collecting critical climate data along the way. The saildrone Surveyor followed this in January 2021, equipped with sonar to map the seafloor at depths up to 23,000 feet (7,000 meters).
Autonomous ships are part of a new wave of future exploration vehicles. Vessels equipped as standard with a range of sensors, sophisticated guidance software and powered by renewable energy. Among them is the Mayflower autonomous ship, piloted by an AI captain; it will celebrate the Pilgrims' journey from England to America in 1620 and measure the ocean's health.
But it's not all about history-making or boundary-pushing. Sometimes doing the simple, but urgent tasks is just as important. Razer, for example, is an AI-guided surface drone programed to clean up plastic trash from the sea and collect data about pollution.
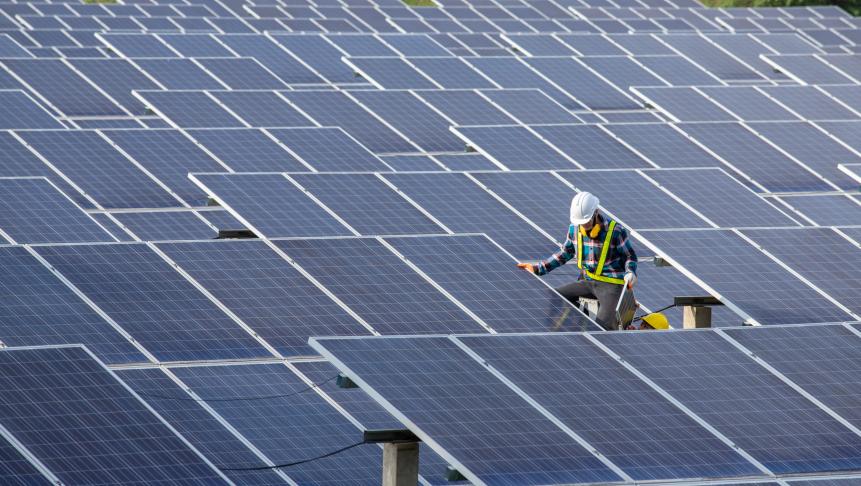

Pramote Polyamate
Engineer checking equipment at a solar power plant.
Even cleaning has a dirty side, it seems, as every year hundreds of Indian sewer workers are killed by poisonous gases while cleaning and removing blockages. Gujarati civic leaders vowed to stop this senseless loss of life by deploying a solar-powered robotic scavenging machine to clear sewers–armed with a gas sensor and video cameras, it can even separate out plastic particles, say its makers.
Anyone looking for a more wholesome use of solar energy should look instead to farming robots. Menial tasks like cutting grass and weed removal are being automated, in the form of the University of Sydney’s eco-friendly RIPPA, to speed up productivity.
RIPPA measures soil moisture and temperature, identifies weeds using a high-speed camera, and delivers highly targeted doses of weed killer and pesticide.
Ladybird is another of the university’s solar-driven robots, designed to maximize crop outputs using lasers, video and hyper-spectral cameras. All-wheel steering is less disruptive to the tilled soil and allows the robot to compensate for unevenly planted rows. Ladybird maps each farm, classifies crops and finds problems.
On its first outing to a farm growing beetroot, onions and spinach, Ladybird operated for three days on one battery charge. Just like any other industry, there are environmental issues on farms and the solar-powered robot could help unlock sustainable cultivation to make food more eco-friendly.