Surasak Suwanmake
Doing Renewables Right
Having a “net-zero future” – where the world isn’t emitting excess carbon dioxide – can seem like a far-off pipe dream.
With sea levels still rising, wildfires becoming more and more frequent – alongside other extreme weather like floods and storms – and biodiversity rapidly dwindling, it’s imperative we focus on expanding renewable energy across the world, increasing energy sources to help mitigate the impact that fossil fuels have on the climate.
There’s already much underway to help curb global warming, including an ambitious plan announced last year which involves expanding renewable energy use across the country.
However, these renewables may not always be as green as we think - and so it’s important to do them right.
One of the primary issues with electric vehicles, for example, is where the battery materials are sourced. Cobalt, nickel, and lithium are the main materials that are used, and these are mined across the world, from the Democratic Republic of Congo to Argentina and Australia. There are very valid concerns over unethical labor in these mines, as well as the long-term impact on the environment. Are electric vehicles really better than diesel and petrol-powered cars if their batteries are from an unsustainable source?

seksan Mongkhonkhamsao
Electric car in charging.
Scientists are racing against the clock to develop sustainable materials, and make existing technology more environmentally friendly, such as renewably powered charging stations that aren’t reliant on coal, better energy storage systems, more efficient car batteries, and batteries that are made from sustainable materials, such as polypeptides.
But that’s just the automobile industry – what about the rest?
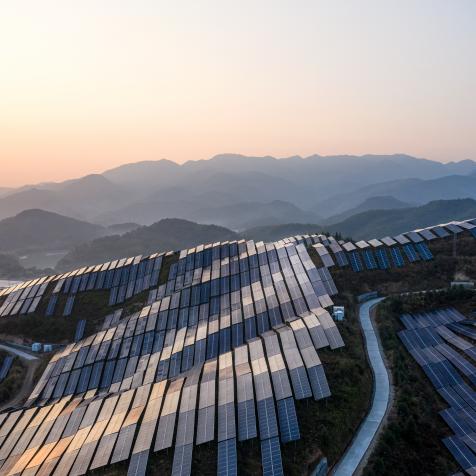
Developing a green future means a vast increase in renewable energy sources, but the new infrastructure will take up vast swathes of land. Unless that is, planners use “smart siting”. This means protecting communities living near developments, conserving land, and not harming biodiversity. Offshore wind plays a big part in reaching goals, but when it comes to onshore energy production, the Princeton Net Zero America report estimates a 228,000-square-mile footprint, greater than Colorado and Wyoming combined.

Abstract Aerial Art
Wind turbines
Certain places should be avoided when developing renewable energy, and so finding land such as mine sites, landfills, and contaminated land – all known as degraded land which is hard to use – is key. Globally, there is enough of this land in the world to meet the Paris climate goals 17 times over. In the US, there is enough of this land to supply 1.3 million megawatts of solar energy.
It’s vital to plan ahead if we really want to “go green”. More than half of US states have already developed siting guidelines; Massachusetts for example has adopted a program to incentivize renewable energy development on brownfields, whereas Nevada, Virginia, and West Virginia are identifying ways to harness solar power to bring jobs to coal communities. But that also means many haven’t prioritized responsible siting.
Many challenges come with ramping up renewable energy, and it’s paramount that these are addressed now, while these technologies are being developed and the transition is taking place, rather than in years ahead when we are looking back on what we should have done